Sweden has long been the poster child of the ‘mixed economy’, the social democrat state – where capitalism is ‘moulded’ to provide a welfare state, equality and decent working and living conditions for the majority. The 2018 general election result has put that story to bed.
In yesterday’s election, the Social Democrats, the supposed standard-bearer of the ‘mixed economy’, remained the largest party with just over 28% of the vote. But this was its lowest share in an election since 1908. The main pro-business party, the so-called Moderates, also lost votes, coming in with 19.7%. Cutting through both these parties, who have alternated for decades in controlling government, was the rise of Sweden’s so-called Democrats (an oxymoron), an anti-immigrant party with neo-Nazi roots, which polled 17.7%. The smaller parties of the centre-right and the left also gained – the Left party jumping to 8%. The middle-of the road Green party was run over and nearly failed to gain the 4% necessary to enter parliament. The two alliances of the social democracy and the pro-business parties are virtually tied with 40% of the vote each – leaving the Democrats with the balance of power in the new parliament. Such is the impasse.
It was an illusion anyway about Sweden being the ‘third way’ between untrammelled free market capitalism and command economy autocratic Communism. The great gains of the Swedish labour movement in the early 20th century have slowly been reversed. And the post-war diversion to public services of some of the profits of the Swedish engineering and manufacturing (owned by a handful of families) stopped decades ago. Just as in other capitalist economies, the polices of neoliberalism – a reversion to free markets, low taxation for the rich and corporations, cuts in the welfare state and in real wages, rising inequality etc – have been operating in Sweden since the mid 1990s.
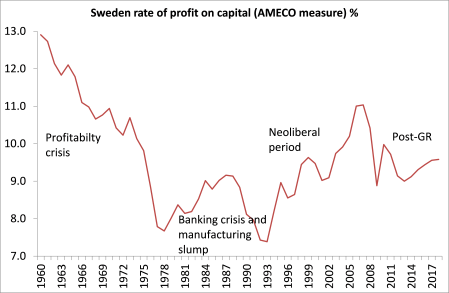
Why were neo-liberal policies introduced in Sweden? As in other capitalist economies, the profitability of capital fell sharply from the mid-1960s (to the mid-1990s in the case of Sweden). After a credit boom that went bust and a major banking crisis, Sweden’s famed manufacturing sector took a massive dive. It was then that Sweden’s major parties, the Social Democrats and Moderates, firmly adopted policies to boost the rate of profit for capital at the expense of the welfare state and public services.
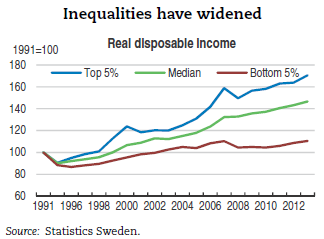
Sweden may still have a more ‘equal’ income and wealth distribution than the US and the UK, but it is still very unequal – and inequality has been rising the fastest since the 1990s of all advanced capitalist economies. In 2012, the average income of the top 10% of income earners was 6.3 times higher than that of the bottom 10%. This is up from a ratio of around 5.75 to 1 in the 2007 and a ratio of around 4 to 1 during much of the 1990s. Sweden’s richest 1% of earners saw their share of total pre-tax income nearly double, from 4% in 1980 to 7% in 2012. Including capital gains, income shares of the top percentile reached 9% in 2012. During the same time, the top marginal income tax rate dropped from 87% in 1979 to 57% in 2013.
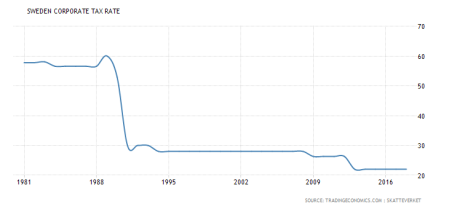
In Sweden, like in most other Nordic countries, tax reforms over the 1990s have decreased the tax burden for wealthier households, e.g. by decreasing capital taxation and lowering or abandoning wealth taxation. At the same time, there have been cuts in welfare benefits for the poor.
What is not often known is that Sweden is no longer an epitome of state provision. The country is one of the world leaders in having public services supplied by the private sector, paid for by the government. About one-third of all Swedish secondary schools are so-called ‘free schools’, with the majority of them run by for-profit companies, while about 40% of primary healthcare providers are privately owned. Public provision has been outsourced to the detriment of quality. Sweden’s schools have slipped from being one of the world’s best in international ratings to “one of the most mediocre”.
The rise of the Democrats follows the pattern of so-called populism that we have seen in Germany, France, Italy, Denmark and other EU countries, as well as with Brexit in the UK and Trump in the US. It is the product of the failure of capitalism to deliver after the end of the Golden Age in the mid-1960s, but particularly after the global financial crash, the Great Recession and the ensuing Long Depression.
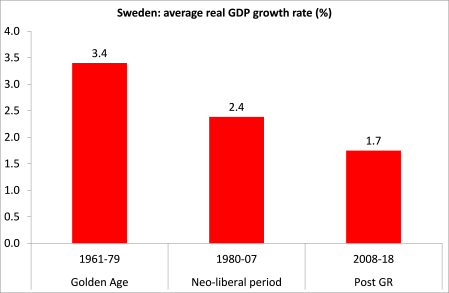
Swedish capitalism, somewhat like Germany (only much smaller), has done better than most other capitalist economies since 2008. But even in Sweden, the rate of economic growth has slowed in the last few decades and particularly since 2008.
Unemployment may be low by EU standards but the official figure hides those on work programmes (German-style) and those on sick benefits. As in Germany, many jobs are now ‘precarious’ and low-paid, particularly in the small towns. And there have been significant public spending cuts on hospitals, schools, housing, pensions and transport.
And then there is immigration. Over 600,000 immigrants from the Middle East have entered the country since the Syrian/Iraq disaster (graph below). Many immigrants are young single men and they have helped capitalist enterprises and the state sector overcome an acute labour shortage for low skilled work. But the amount of immigrants per head of population is way more than in any other European economy and it has increased pressure on those public services, already suffering from neo-liberal measures.
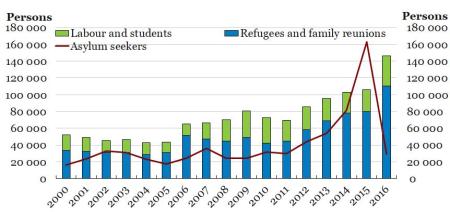
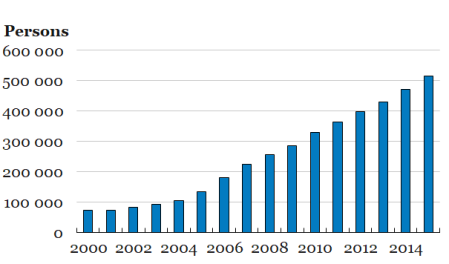
There has been a massive housing boom driven by low interest rates and credit. That has benefited the middle and upper classes but the working class and immigrants struggle for proper housing (graph – waiting list for rented housing in Stockholm).
Sweden is still growing much faster than much of the rest of Europe, but it is highly dependent on the growth of world trade and the strength of economic activity in Europe. The strong growth has been driven again by a credit-fuelled consumer boom as in the 1980s, as well as from the extra value from immigrant labour.
Stockholm has the second most inflated housing market in the world, while the banking sector booms. The Swedish banks currently have assets that are four times the national GDP, second only to Switzerland. The 1980s are repeating themselves.
Real GDP growth seems strong at over 3% a year. But if you strip out the impact of extra immigrant labour, real GDP growth per person is much lower (below 1% in 2017). Real per capita growth is seen averaging just 1% in the decade through 2026, according to the Swedish National Institute of Economic Research.
The small towns in Sweden have experienced low wages, poorer services and then were faced with an influx of new immigrants. This was the breeding ground for the Democrats’ racist and nationalist message of ‘Sweden for Swedes’. The Social Democrats are now paying for their support of capitalism and neo-liberal policies of the last 20 years.
1 comment:
Thanks for posting this Richard. Great article ! Especially since it takes a good amount of effort for people living in the U.S. to find accurate info about what is really happening in Europe and the rest of the world for that matter.
Post a Comment