Last week, the OECD published its latest World Economic Outlook. WARNING GRAPHICS OVERLOAD AHEAD!
The OECD’s economists reckon that “The global economy is now growing at its fastest pace since 2010, with the upturn becoming increasingly synchronised across countries. This long-awaited lift to global growth, supported by policy stimulus, is being accompanied by solid employment gains, a moderate upturn in investment and a pick-up in trade growth.”
While world economic growth is accelerating a bit, the OECD reckons that “on a per capita basis, growth will fall short of pre-crisis norms in the majority of OECD and non-OECD economies.” So the world economy is still not yet out of the Long Depression that started in 2009.
The OECD went on: “Whilst the near-term cyclical improvement is welcome, it remains modest compared with the standards of past recoveries. Moreover, the prospects for continuing the global growth up-tick through 2019 and securing the foundations for higher potential output and more resilient and inclusive growth do not yet appear to be in place. The lingering effects of prolonged sub-par growth after the financial crisis are still present in investment, trade, productivity and wage developments. Some improvement is projected in 2018 and 2019, with firms making new investments to upgrade their capital stock, but this will not suffice to fully offset past shortfalls, and thus productivity gains will remain limited.”
The OECD also thinks that much of the recent pick-up is fictitious, being centred on financial assets and property. “Financial risks are also rising in advanced economies, with the extended period of low interest rates encouraging greater risk-taking and further increases in asset valuations, including in housing markets. Productive investments that would generate the wherewithal to repay the associated financial obligations (as well as make good on other commitments to citizens) appear insufficient.” Indeed, on average, investment spending in 2018-19 is projected to be around 15% below the level required to ensure the productive net capital stock rises at the same average annual pace as over 1990-2007.
The OECD concludes that, while global economic growth will be faster in 2017 and 2018, this will be the peak. After that, world economic growth will fade and stay well below the pre-Great Recession average. That’s because global productivity growth (output per person employed) remains low and the growth in employment is set to peak. That’s a ‘slow burn’ of slowing economic growth.
But even more worrying for global capitalism is the prospect of a new economic slump, now that we are some nine years since the last one. In a chapter of the World Economic Outlook, the OECD’s economists raise the issue of the very high levels of debt (both private and public sector) that linger on since 2009. “Despite some deleveraging in recent years, the indebtedness of households and nonfinancial businesses remains at historically high levels in many countries, and continues to increase in some.” The debt of non-financial firms (NFC) rose relative to GDP during the mid-2000s, generally peaking at the onset of the global financial crisis and remaining stable thereafter.
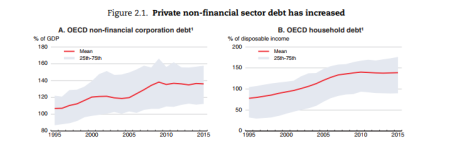
After a limited downward adjustment during the post-crisis period, NFC debt-to-GDP ratios have increased again since.
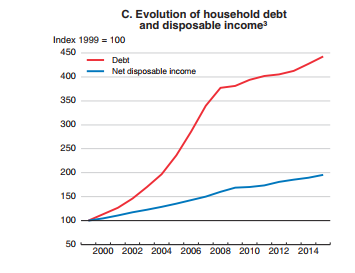
Household debt-to-income ratios also rose significantly up to 2007 and stabilised thereafter at historically high levels in most advanced economies. The rise in the debt-to-income ratio was driven by the acceleration in debt accumulation prior to the crisis, with subdued household income growth impeding deleveraging thereafter.
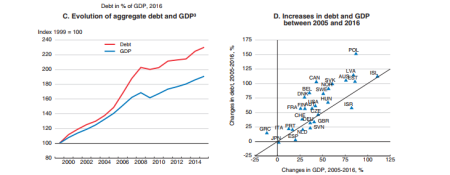
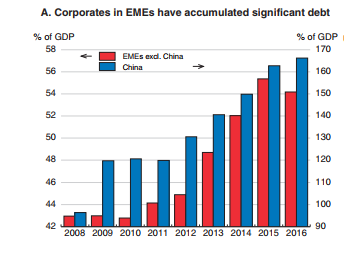
And as I have reported before in previous posts, non-financial companies (NFC) in the so-called emerging economies have sharply increased their debt burdens over the last nine years, so that now, ‘rolling over’ this debt as it matures for repayment amounts to about half of the gross issuance of international debt securities in 2016. In other words, debt is being issued to repay earlier debt at an increasing rate.
The OECD points out that there is empirical evidence that high indebtedness increases the risk of severe recessions. Also, if the prices of ‘fictitious’ assets like property or stocks get well out of line with the value of productive assets (ie capital investment), that is another indicator of a coming recession. Currently, there is no OECD economy in recession (defined as two consecutive quarters of a fall in GDP), but the global house price index is reaching a peak level over the trend average that has signalled recessions in the past.
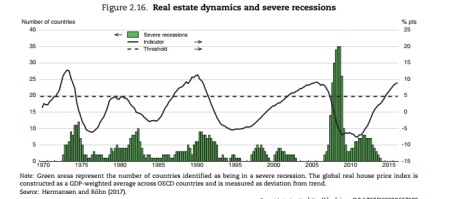
Credit is necessary to capitalism to overcome the ‘lumpiness’ in capital investment and smooth over cash liquidity. But as Marx argued, ‘excessive’ credit expansion is a sign that the profitability of productive investment is falling. As the OECD puts it: “If borrowing is well used, higher indebtedness contributes to economic growth by raising productive capacity or augmenting productivity. However, in many advanced economies, the post-crisis build-up of corporate debt has not translated into a rise in corporate capital expenditure.”
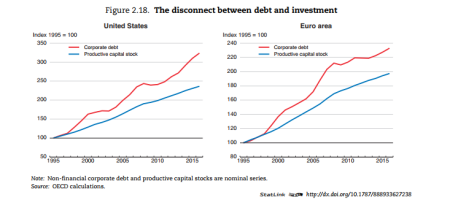
So the OECD concludes that the post-crisis combination of rising corporate debt and historically high share buybacks may suggest that, rather than financing investment, firms took on debt to return funds to shareholders. This reflects “pessimism about future demand and economic growth, leading corporations to defer capital spending and return cash to their shareholders for want of attractive investment opportunities.” Moreover, firms with a persistently high level of indebtedness and low profits can become chronically unable to grow and become “zombie” firms. And zombie “congestion” may thus reduce potential output growth by hampering the productivity-enhancing reallocation of resources towards more dynamic higher productivity firms.
So the OECD story is that world economic growth is picking up and there is little sign of any slump in production in the immediate future, even if growth may stay well below the pre-crisis average. But there are risks ahead because the still very high levels of debt and speculation in financial assets that could come a cropper if profitability and growth should falter.
This is much the same story that the IMF told in latest IMF report on Global Financial Stability that I referred to in a recent post. As the IMF put it: “Private sector debt service burdens have increased in several major economies as leverage has risen, despite declining borrowing costs. Debt servicing pressure could mount further if leverage continues to grow and could lead to greater credit risk in the financial system.”
The IMF comments: “While debt accumulation is not necessarily a problem, one lesson from the global financial crisis is that excessive debt that creates debt servicing problems can lead to financial strains. Another lesson is that gross liabilities matter. In a period of stress, it is unlikely that the whole stock of financial assets can be sold at current market values— and some assets may be unsellable in illiquid conditions.” So “if there are adverse shocks, a feedback loop could develop, which would tighten financial conditions and increase the probability of default, as happened during the global financial crisis.”
The IMF sums up the risk. “A continuing build-up in debt loads and overstretched asset valuations could have global economic repercussions. … a repricing of risks could lead to a rise in credit spreads and a fall in capital market and housing prices, derailing the economic recovery and undermining financial stability.”
The IMF posed an even nastier scenario for the world economy than the OECD by 2020. Yes, the current ‘boom’ phase can carry on. Equity and housing prices can continue to climb. But this leads to investors to drift beyond their traditional risk limits as the search for yield intensifies despite increases in policy rates by central banks. Then there is a ‘Minsky moment’.
There is a bust, with declines of up to 15 and 9 percent in stock market and house prices, respectively, starting at the beginning of 2020. Interest rates rise and debt servicing pressures are revealed as high debt-to-income ratios make borrowers more vulnerable to shocks. “Underlying vulnerabilities are exposed and the global recovery is interrupted.” The IMF estimates that the global economy could have a slump equivalent to about one-third as severe as the global financial crisis of 2008-9 with global output falling by 1.7 percent from 2020 to 2022, relative to trend growth.
Will the high debt in the corporate sector globally eventually bring down the house of cards that is built on fictitious capital and engender a new global slump? When is credit excessive and financial asset prices a bubble?
The key for me, as readers of this blog know, is what is happening to the profitability of capital in the major economies. If profitability is rising, then corporate investment and economic growth will follow – but also vice versa. But if profitability and profits are falling, debt accumulated will become a major burden. Eventually the zombies will start to go bankrupt, spreading across sectors and a slump will ensue. Financial prices will quickly collapse toward the real value of their underlying productive assets.
Indeed, according to Goldman Sachs economists, the prices of financial assets (bonds and stocks) are currently at their highest against actual earnings since 1900!
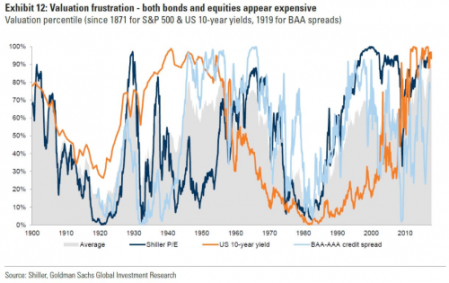
What the OECD and IMF reports show is that if there is a downturn in profitability, the next slump will be severe, given that private debt (both corporate and household) has not been ‘deleveraged’ in the last nine years – indeed on the contrary. As I said, in my paper on debt back in 2012: “Capitalism is now left with a huge debt burden in both the private and public sector that will take years to deleverage in order to restore profitability. So, contrary to the some of the conclusions of mainstream economics, debt (particularly private sector debt) does matter.”
For now, the world economy is making a modest recovery from the stagnation that appeared to be setting in from the end of 2014 to mid-2016. The Eurozone economic area is seeing an acceleration of growth to its highest rate since the end of the Great Recession.
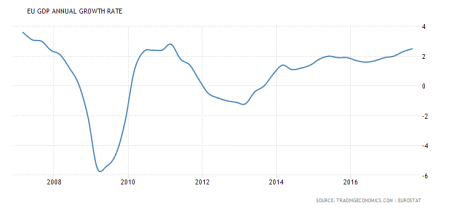
Japan too is picking up, based on a weak currency that is enabling exports to be sold. And the latest figures for the US show an annualised rise of 3.3% in third quarter of 2017, putting year on year growth at 2.3%, still below the rates achieved in 2014 but much better than in 2016 (1.6%). And the forecast for this current quarter is for similar.
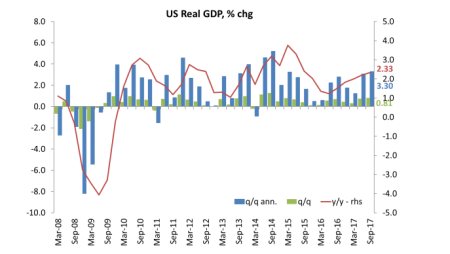
As for corporate profits and investment, the latest data show that US corporate profits were rising at over 5-7% yoy before tax, although stripping out the mainly fictitious profits of the financial sector reveals that the mass of profit is still well below the peak of end-2014.
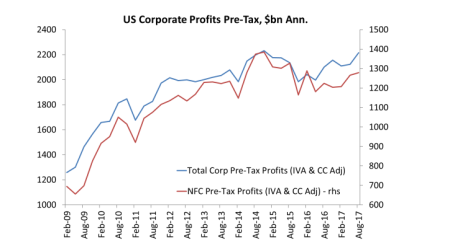
And as I showed in a recent post, profitability has fallen since 2014.

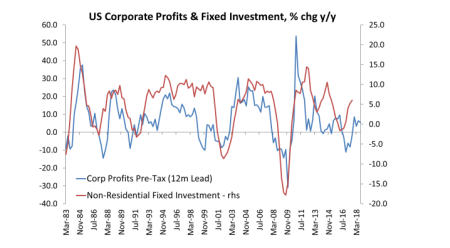
There is a high correlation and causality between the movement of profits and productive investment.
And that is confirmed in the latest data for the US. As corporate profits have recovered from the slump of 2015-16, so business investment has made a modest improvement.
As for global corporate profits, we don’t have all the data for Q3 2017, but it looks as though it will continue to be on the up.
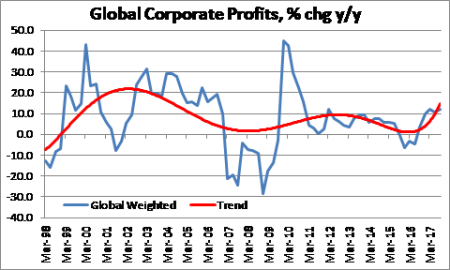
So overall, global economic growth has improved in 2017 and, so far, looks likely to do so in 2018 too. Corporate profits are rising and that should help corporate investment. But profitability of capital remains weak and near post-war lows and corporate debt has never been higher.Any sharp upswing in interest rate costs (and the US Fed continues to hike) will increase the debt servicing burden. So if corporate profits should peak and falter in the next year or so, a major recession will be on the agenda.
No comments:
Post a Comment